In the context of the accelerated transformation of the medical and health industry towards precision, personalization, and intelligence, medical silicone injection molding technology, with its biocompatibility, precision molding capabilities, and functional expandability, is becoming a core driving force in the manufacturing of high-end medical devices. From implantable devices to in vitro diagnostic consumables, from smart wearable medical devices to personalized orthopedic appliances, liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding technology is breaking through the boundaries of traditional materials and processes, opening a new chapter in medical manufacturing. The following will analyze the future development trends of medical silicone injection molding from four dimensions: material innovation, process upgrading, intelligent integration, and green manufacturing.
1. Material Innovation: Dual-Wheel Drive of High Functionality and Biodegradability
In the future, medical silicone materials will evolve in depth towards high functionality and environmental friendliness. Nano-modification technology, by introducing inorganic nanoparticles (such as silica and carbon nanotubes), can increase the tensile strength of silicone to over 15 MPa while maintaining its flexibility, meeting the high-strength requirements of artificial joints and orthopedic implants. For example, the coating layer of pacemaker leads has already adopted LSR materials with a Shore A hardness of 30-50, and its tear resistance can withstand long-term heartbeats. In the future, by integrating conductive silicone with real-time monitoring functions, a "structure-function" integration will be achieved.
The research and development of biodegradable silicone focus on environmental protection and sustainability. Composite silicone materials based on polylactic acid (PLA) or polycaprolactone (PCL) have completed preclinical trials and can gradually degrade into non-toxic small molecules in the body, providing environmentally friendly solutions for absorbable sutures and temporary stents. In addition, the breakthrough of platinum-free catalyst systems has reduced the curing temperature of silicone to below 80 °C, reducing energy consumption and the risk of heavy metal residues.
2. Process Upgrading: Micro-Nano Precision and Multi-Component Composite Molding
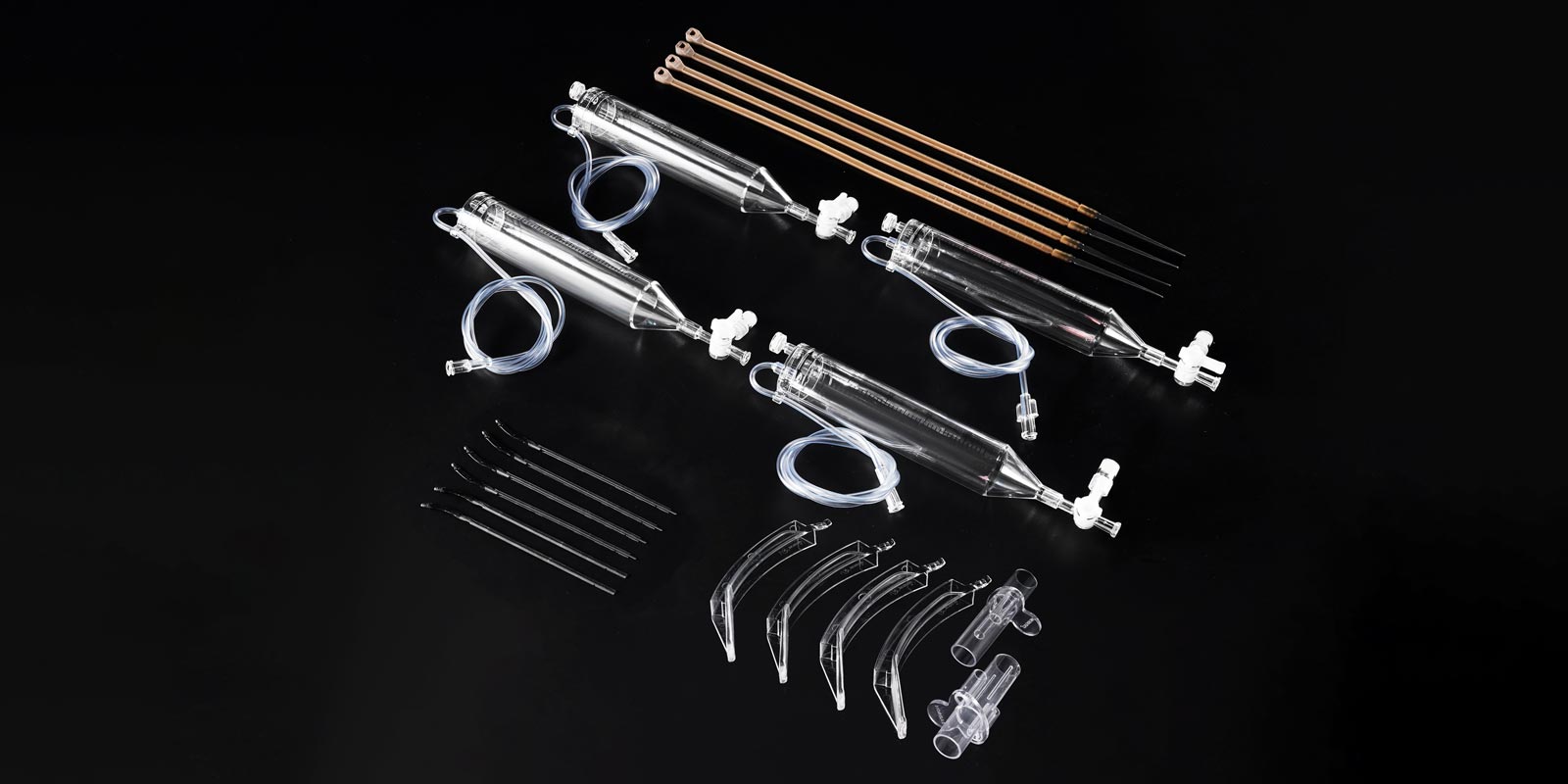
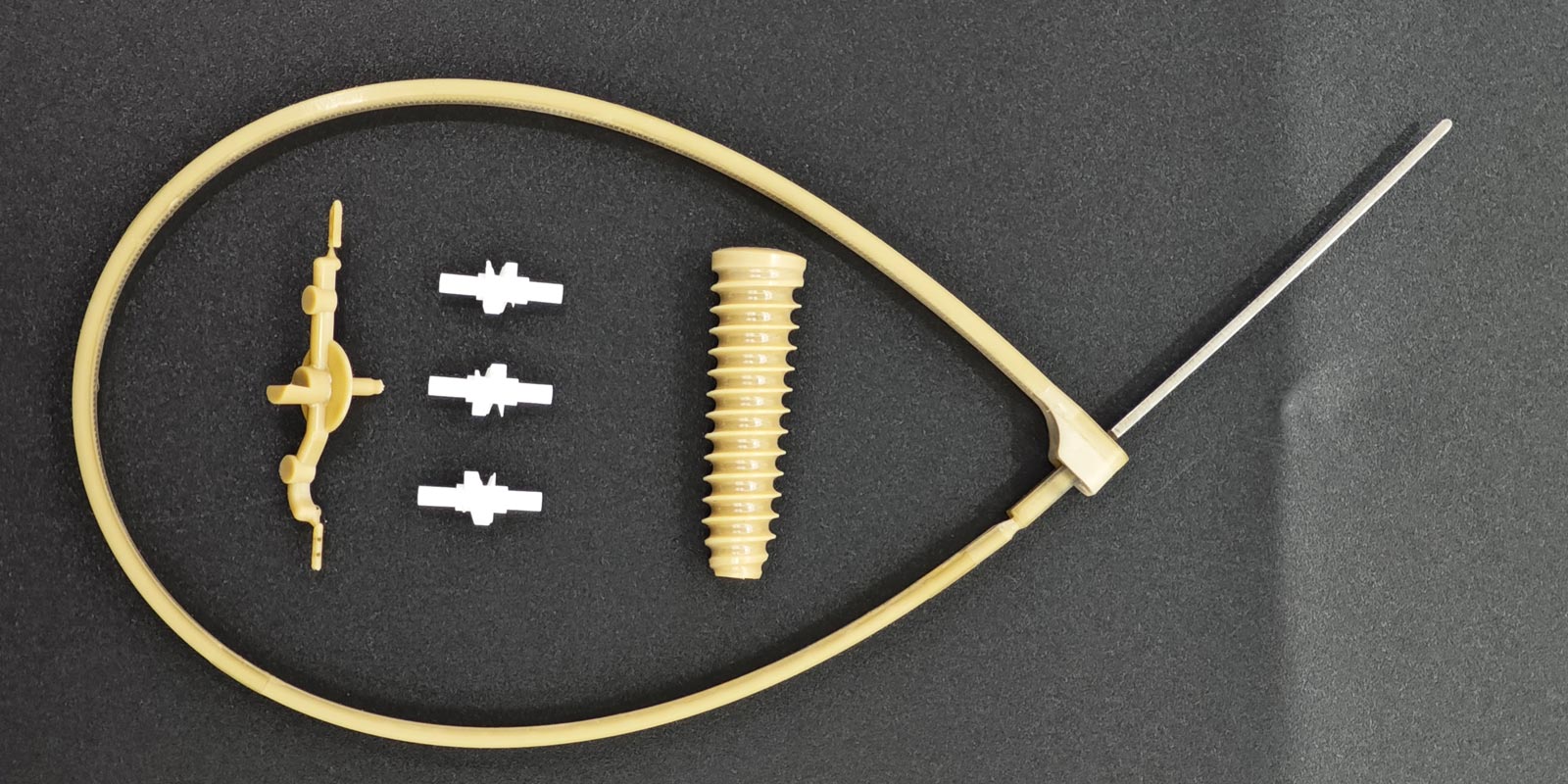
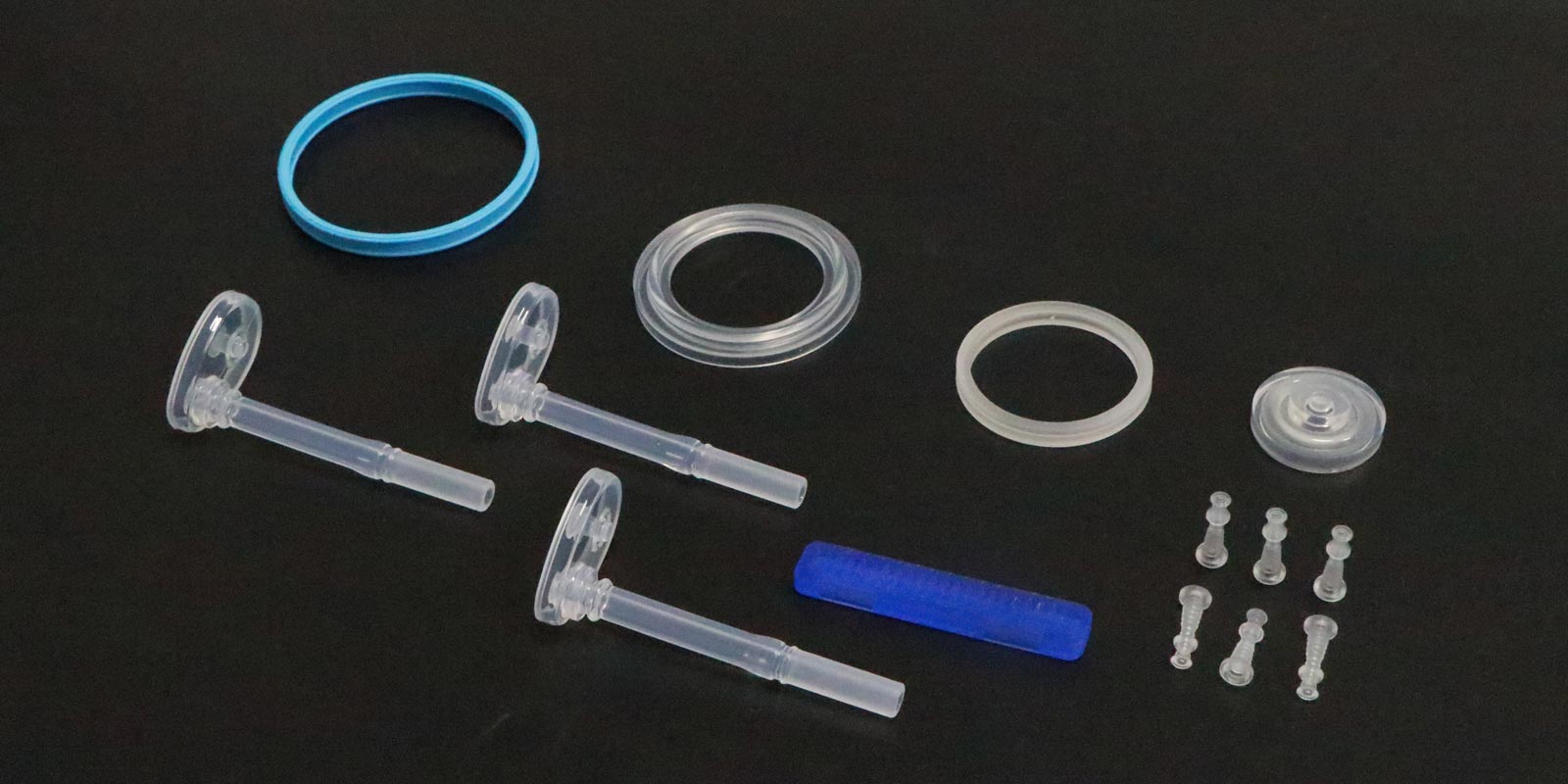
With the increasing demand for miniaturization in fields such as microelectronics and neurointervention, liquid silicone injection molding machines are advancing towards a position repeatability of ±0.01 mm. Multi-component injection molding technology can achieve the composite molding of silicone with different hardness and colors. For example, the "inner layer PA rigid support + outer layer LSR soft contact" structure of vascular intervention catheters has increased the bending fatigue life to over 1000 times through secondary injection molding. Intelligent temperature control systems and energy recovery technologies have shortened the molding cycle of a single product to 15 seconds while reducing energy consumption by 30%.
Digital twin technology optimizes mold design through virtual simulation, compressing the trial mold cycle from several weeks to within 72 hours and significantly reducing development costs. For example, by simulating runner balance and cooling systems, a certain enterprise has increased the yield rate of a smart catheter mold from 82% to 98%. In addition, the combination of 3D printing and liquid silicone injection molding is reshaping the paradigm of personalized medical manufacturing. Combined with patient CT/MRI data, it can customize the production of orthopedic appliances, prosthetic liners, and other implants. The microstructure surface (such as a 0.3 mm deep serrated interlocking structure) increases the bonding strength to over 5 N/mm².

3. Intelligent Integration: Sensor Integration and Data-Driven
In the field of smart medical devices, LSR watch straps embedded with pressure-sensing pads can monitor the wearing fit in real time, and the data is transmitted to the cloud via Bluetooth, forming a closed loop of "prevention-diagnosis-intervention." For example, a certain smart dressing integrates temperature and humidity sensors into the silicone substrate, which can dynamically monitor the wound healing environment and automatically trigger an alarm when the risk of infection increases. In the field of in vitro diagnostics, the LSR sealing layer of microfluidic chips has been controlled to a thickness of less than 0.1 mm, and combined with ultraviolet curing processes, the production efficiency of nucleic acid detection kits has been increased by 40%.
The introduction of AI algorithms further optimizes the injection molding process parameters. By using machine learning to analyze historical production data, the system can automatically adjust key parameters such as injection speed and holding pressure, stabilizing the product dimensional accuracy within ±0.02 mm. After applying this technology, a certain enterprise has reduced the scrap rate of a certain cardiac occluder from 3.2% to 0.5%, saving more than 2 million yuan in costs per year.
4. Green Manufacturing: Closed-Loop Recycling and Low-Carbon Production
The tightening of environmental regulations is forcing industry technological iterations. The EU's REACH regulation has added four new restricted substances, driving enterprises to develop platinum-free catalyst systems, reducing the curing temperature to below 80 °C and energy consumption. Closed-loop recycling systems achieve a material recovery rate of 95% through chemical depolymerization, reducing dependence on raw materials such as metallic silicon. For example, a certain enterprise's silicone waste recycling line can convert production scraps into recycled LSR raw materials, with performance differences of less than 5% from virgin materials.
The revised version of China's "Medical Silicone Product Industry Standard" has strengthened the traceability requirements for biological safety, prompting enterprises to establish a carbon footprint management system from raw materials to finished products. By adopting solar power and waste heat recovery devices, a certain enterprise has reduced the carbon emissions per ton of products from 2.8 tons to 1.2 tons, achieving the industry's 2030 emission reduction target in advance.
Conclusion: Technological Integration Reshaping the Medical Ecosystem
The future of medical silicone injection molding is one of deep integration of material science, intelligent manufacturing, and clinical needs. From nano-modification to intelligent production, from personalized customization to green manufacturing, technological breakthroughs will continue to expand the boundaries of medical applications. As the global high-end medical market pursues "safety, precision, and intelligence," liquid silicone injection molding technology will undoubtedly play a more critical role, injecting innovative momentum into human health.













 Home
Home
