In the medical field, injection molding technology has become a core driving force for technological progress. From precision instruments in operating rooms to rehabilitation equipment used by patients daily, from sophisticated diagnostic devices to implants safeguarding life safety, medical injection molding shapes countless standardized parts by injecting molten plastic into high-precision molds. These products not only need to meet strict biocompatibility requirements but also maintain stable performance under extreme conditions. This article will systematically review the typical application scenarios of medical injection-molded products and reveal how they support the operation of the modern healthcare system.
I. Basic Medical Consumables: The First Line of Defense Safeguarding Life Safety
-
Injection Systems
Syringes and infusion sets are classic examples of medical injection molding. Made from polypropylene (PP) or polyethylene (PE), the syringe barrel body produced through thin-wall injection molding can have a wall thickness of less than 0.8 mm, ensuring precise drug delivery. The test reaction cups produced by the Chen Hsong SPARK EH electric injection molding machine, using a 48-cavity mold, achieve an ultra-short cycle time of 6.5 seconds, with a daily production capacity exceeding 100,000 pieces, meeting the demand for large-scale nucleic acid testing. The connectors of infusion sets adopt gas-assisted injection molding technology, forming hollow channels within complex flow path structures, which not only reduces weight but also improves sealing performance.
-
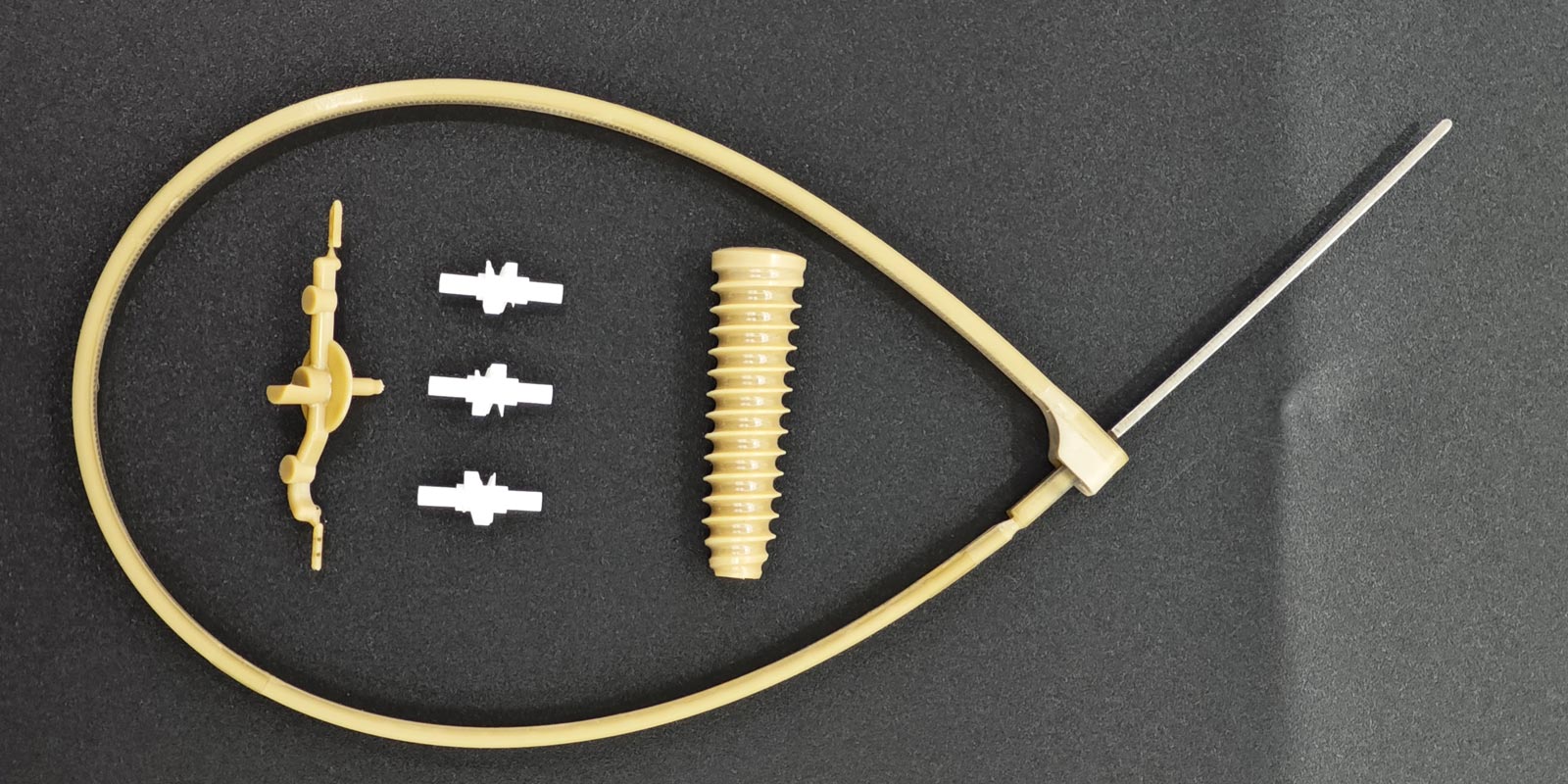
Catheter Systems
From central venous catheters to micro-catheters used in minimally invasive surgeries, injection molding technology has achieved precision breakthrough from the millimeter to the micrometer level. A certain enterprise uses liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding technology to produce urinary catheters. Through two-color injection molding, the soft silicone tube body and the hard connector are integrated into one piece, avoiding the leakage risks associated with traditional assembly processes. Gas-assisted injection molding technology is widely used in the manufacture of catheter shells. By controlling the wall thickness distribution through nitrogen pressure, the product's anti-kinking performance is improved by 40%.
II. Diagnostic Equipment: The Intelligent Eyes Opening the Door to Precision Medicine
-
Imaging Equipment Components
In CT scanners, the precision connectors that link the data acquisition board to the main unit are injection-molded from polyether ether ketone (PEEK). This high-performance polymer can withstand liquid nitrogen cooling at -196°C while maintaining dimensional stability. A certain enterprise has developed an ultra-large housing for MRI machines. Using the Chen Hsong SM2600-TP injection molding machine, it can mold a giant component measuring 1,750 mm × 1,690 mm in one shot, reducing the assembly error from 1.2 mm in traditional processes to 0.05 mm.
-
In Vitro Diagnostic Consumables
The microplates used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) are produced through nano-injection molding. A polypropylene substrate is directly molded into a micro-well array with a pore diameter of 0.2 mm, with a pore diameter deviation controlled within ±0.01 mm. The plastic carriers for blood glucose test strips adopt micro-foaming injection molding technology. Within a 0.3 mm thick substrate, uniformly distributed micro-pores are formed, increasing the reagent reaction speed by 30%.
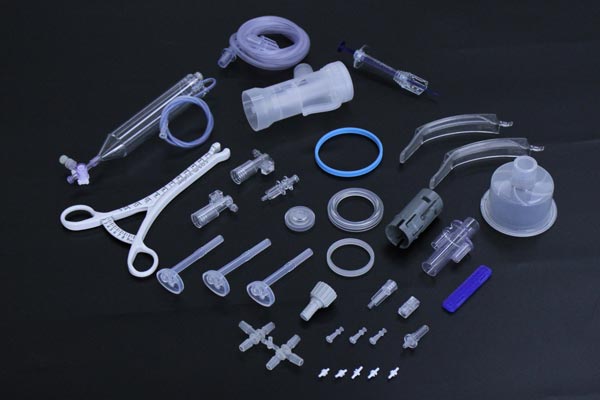

III. Surgical Instruments: Precision Tools Reshaping the Human Body Structure
-
Minimally Invasive Surgical Instruments
The grasping forceps heads used in laparoscopic surgeries are produced through insert injection molding, integrating 316L stainless steel inserts with a polyetherimide (PEI) housing. This design ensures that the instrument maintains a clearance fit of 0.02 mm even after 1,000 cycles of high-temperature steam sterilization at 134°C. A certain enterprise has developed an ultrasonic scalpel handle. Through two-color injection molding, a hard polycarbonate (PC) skeleton is combined with a soft thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) grip, enabling force feedback precision at the 0.1 N level during operation.
-
Implant Manufacturing
Artificial joint prostheses are injection-molded from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), which has a wear resistance 10 times that of ordinary PE. A certain enterprise uses gas-assisted injection molding technology to produce acetabular cups. While maintaining a wall thickness of 12 mm, an internal hollow structure is achieved, increasing the bone ingrowth area by 60%. The housings of pacemakers are injection-molded from medical-grade nylon 12. Through special formulations, they achieve an X-ray transmittance of 98%, facilitating postoperative imaging tracking.
IV. Life Support Systems: The Precise Network Maintaining Vital Signs
-
Respiratory Therapy Equipment
Respirator masks are injection-molded from liquid silicone rubber. By using 3D scanning data of the human face to design the mold, the mask achieves a 98% fit with the face, with an air leakage rate controlled below 3 L/min. A certain enterprise has developed oxygen valve bodies injection-molded from PEEK, which maintain dimensional stability within a temperature range of -40°C to 180°C, ensuring reliable operation in extreme environments such as polar expeditions.
-
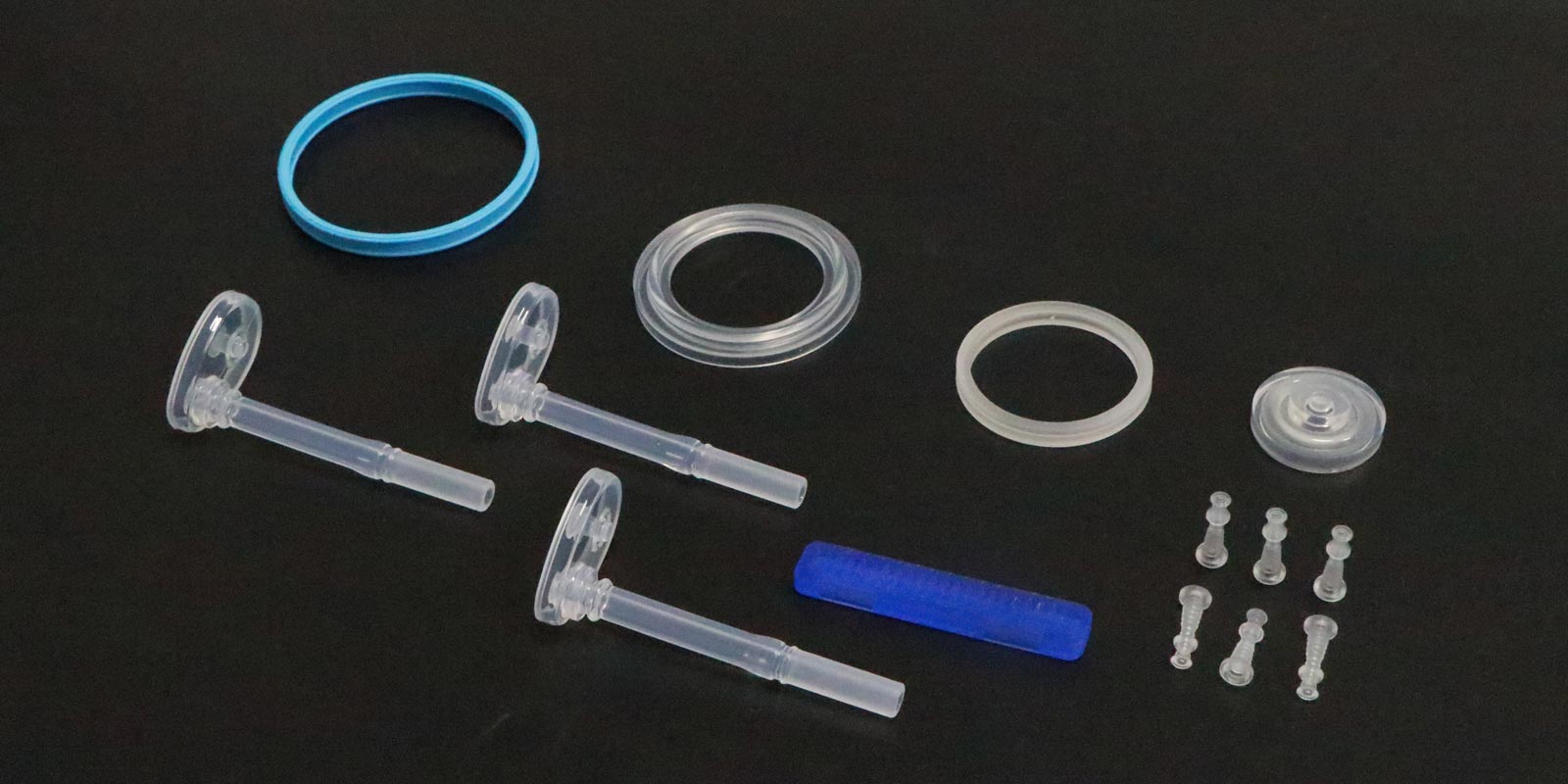
Blood Purification Systems
The end caps of dialyzers are injection-molded from a PC/ABS alloy. Through special formulations, they achieve compatibility with anticoagulants, reducing the thrombus formation rate to 0.05%. The connectors of blood circuit tubes are injection-molded from TPE. Through two-color molding, a 0.5 mm soft layer is coated on the surface of the hard connector, ensuring both connection strength and comfortable insertion and removal.
V. Innovative Applications: Pioneering Explorations Breaking the Boundaries of Healthcare
-
Wearable Medical Devices
The housings of smart wristbands are injection-molded from thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). Through micro-injection molding, an optical sensor window is integrated within a 0.8 mm wall thickness, improving the accuracy of heart rate monitoring to 99.2%. A certain enterprise has developed insulin pump bases. Using nano-injection molding technology, a metal battery compartment is combined with a plastic housing, achieving an IP68 waterproof rating and withstanding a water pressure of 10 meters depth.
-
3D Printing-Assisted Injection Molding
In the custom manufacturing of prosthetic limbs, a 3D-printed model of the patient's limb is first created, which is then used as a master model to develop an injection mold. This hybrid process reduces the customization cycle of prosthetic sockets from 2 weeks to 72 hours and cuts material costs by 60%. A certain enterprise has developed injection molds for titanium alloy implants. By using selective laser melting (SLM) technology to manufacture conformal cooling channels, the molding cycle is shortened by 40%.
Conclusion: Precision Manufacturing Shapes the Future of Healthcare
Medical injection molding technology is evolving towards higher precision, more complex structures, and smarter production. Intelligent injection molding systems developed by enterprises like Chen Hsong, which integrate AI process optimization algorithms, have improved product yield rates to 99.95%. With the expanding applications of biodegradable materials (such as polycaprolactone, PCL) and conductive plastics (such as poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate, PEDOT:PSS), medical injection-molded products are evolving from passive devices to active therapeutic carriers. In this revolution of precision manufacturing, every injection-molded part carries the sacred mission of safeguarding life, jointly building a solid foundation for modern healthcare.
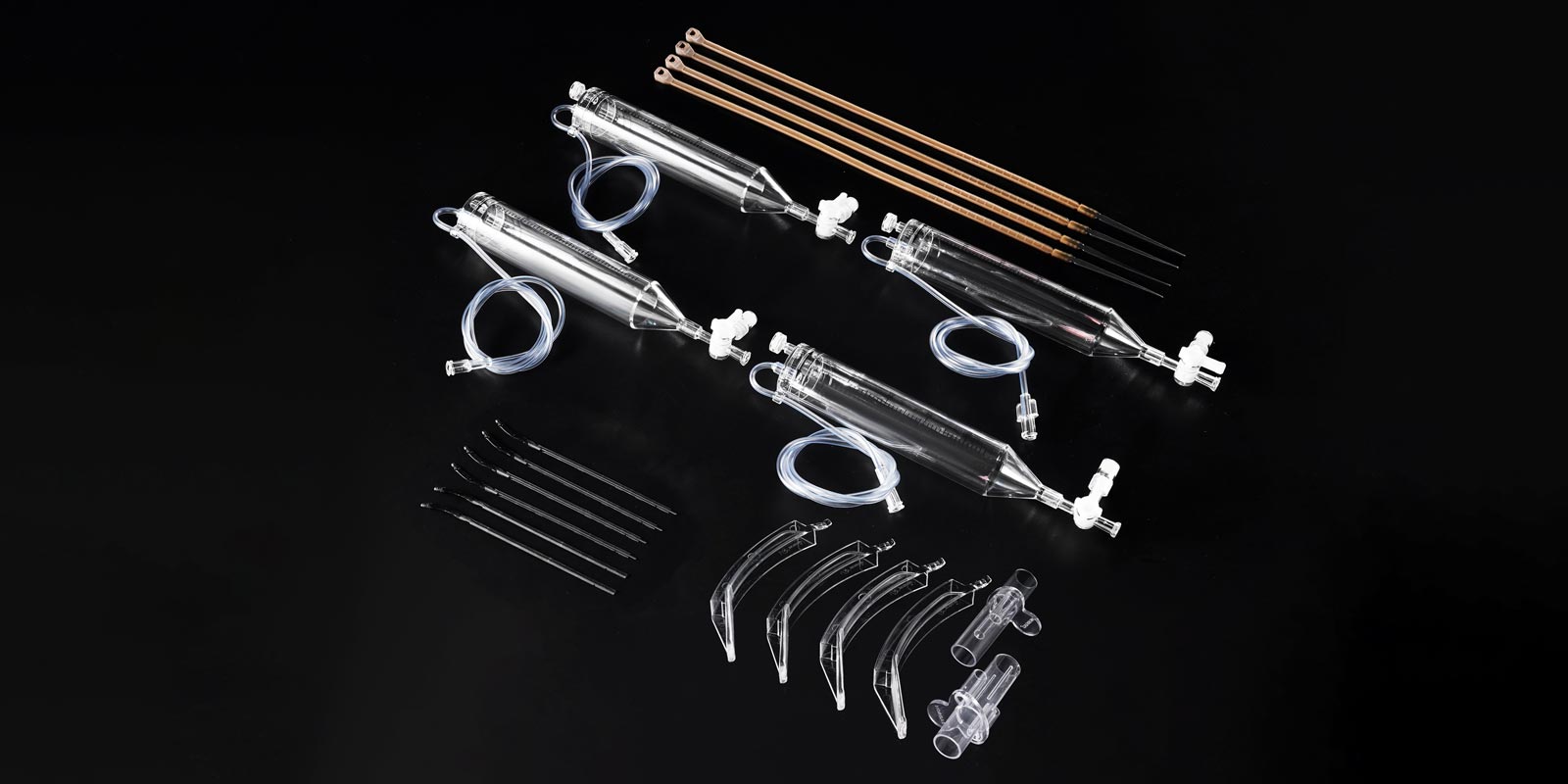













 Home
Home
