Medical injection molding is a core process in manufacturing medical devices, covering products such as syringes, infusion sets, surgical instrument components, and implant casings. These items demand high precision and cleanliness due to their direct impact on patient safety, necessitating strict adherence to standards like ISO 13485 throughout production. This article dissects the five critical stages of medical injection molding and their technical requirements.
1. Raw Material Preparation and Pretreatment: Laying the Quality Foundation
Material selection directly affects product performance. Common medical-grade materials include polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), polyethylene (PE), and medical silicone, all requiring biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and transparency.
Key Controls:
-
Material Validation: Ensure FDA or CE certification for non-toxicity and hypoallergenicity.
-
Drying: Materials like PC and PA, prone to moisture absorption, must be dried at 80–120°C for 4–6 hours to prevent bubbles or silver streaking during molding.
-
Coloring and Additives: Use medical-grade color masterbatches and avoid plasticizers that may leach.
Case Study: A company faced mass recalls after failing to dry materials adequately, resulting in air bubbles in infusion connectors and losses exceeding $1 million.
2. Mold Design and Manufacturing: Balancing Precision and Durability
Medical molds demand ultra-high precision (±0.005mm), corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning, with lifespans exceeding 500,000 cycles.
Design Essentials:
-
Runner Systems: Optimize hot or cold runners to minimize weld lines and stress concentration.
-
Venting: Add vents at parting lines or cores to prevent gas trapping, which causes burn marks or short shots.
-
Ejection Mechanisms: For thin-walled or complex parts (e.g., minimally invasive tools), incorporate lifters or slides for smooth demolding.
Technological Breakthrough: A mold maker reduced the molding cycle of syringe pistons by 15% and lowered defect rates by optimizing runner design via simulation software.
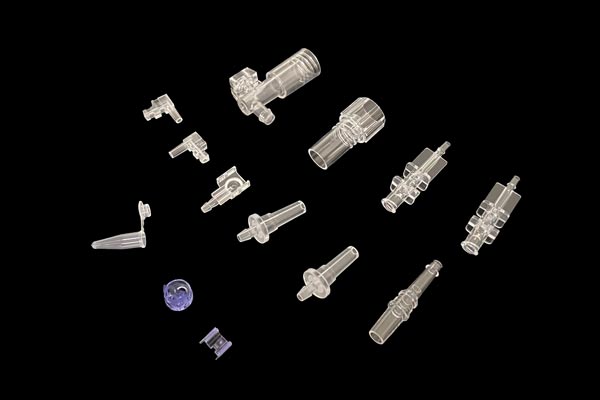

3. Injection Molding Stage: The "Golden Triangle" of Parameter Control
Precision control of temperature, pressure, and speed is vital for product consistency.
Critical Parameters:
-
Melt Temperature: Set according to material properties (e.g., 200–240°C for PP, 280–320°C for PC). Excessive heat causes degradation; insufficient heat reduces flowability.
-
Injection Pressure and Speed: Use multi-stage injection (slow-fast-slow) to avoid turbulent melt fronts and internal stress.
-
Packing and Cooling: Ensure packing time covers shrinkage, and cooling time guarantees full solidification to prevent warping.
Smart Manufacturing: Some firms employ AI-powered injection machines to adjust parameters in real time, cutting defect rates from 3% to 0.5%.
4. Post-Processing and Inspection: The Ultimate Zero-Defect Safeguard
Post-molding processes include deburring, cleaning, and sterilization, followed by rigorous inspections.
Key Steps:
-
Deburring and Polishing: Use mechanical grinding or laser deburring to avoid contamination from manual operations.
-
Cleaning and Drying: Clean with purified water or medical-grade agents, then dry in cleanrooms before packaging.
-
Inspection Standards:
-
Dimensional Checks: Verify critical dimensions via coordinate measuring machines (CMMs).
-
Visual Inspection: Detect flash, short shots, or other flaws using magnifiers or automated optical inspection (AOI).
-
Performance Testing: Simulate real-world conditions for tensile, flexural, and seal tests.
Case Study: A company’s failure to test syringe needle hub seals led to leakage during use, triggering a recall.
5. Packaging and Sterilization: The Final Barrier Against Contamination
Packaging and sterilization must occur in cleanrooms (ISO Class 7 or higher), with methods like ethylene oxide (EO), gamma irradiation, or steam sterilization ensuring sterility.
Requirements:
-
Packaging Materials: Use medical-grade breathable films or aluminum foil composites to prevent moisture ingress during sterilization.
-
Sterilization Validation: Confirm effectiveness via biological or chemical indicators, achieving a sterility assurance level (SAL) of 10⁻⁶.
-
Labeling and Traceability: Each package must include sterilization dates and batch numbers for full lifecycle tracking.
Trend: Growing adoption of biodegradable packaging to reduce medical waste.
Conclusion: From Process Control to Quality Culture
Every stage of medical injection molding must prioritize "zero defects," leveraging automation, digital management, and rigorous training to build a robust quality system. For example, a leading firm improved its process capability index (CpK) from 1.0 to 1.67 using an MES system, achieving a 99.8% first-pass yield. Future advancements, such as 3D-printed molds and AI-driven quality inspection robots, will drive higher precision and lower costs, reinforcing global healthcare manufacturing reliability.













 Home
Home
