In the field of medical equipment manufacturing, injection molding technology has become a core process for manufacturing medical device components due to its high precision, high efficiency, and ability for mass production. From precision surgical instrument handles to complex pharmaceutical packaging components, every step of medical injection molding strictly adheres to industry standards to ensure that products meet requirements for biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and sterility. This article will delve into the complete process of medical injection molding, revealing the technical logic and quality control points behind it.
1. Product Design and Mold Development: Laying a Precise Foundation
The starting point of medical injection molding is product design and mold development, which directly determine the functionality and production feasibility of the product. The design team needs to conduct 3D modeling and structural optimization based on the specific requirements of medical products, such as dimensional accuracy, structural strength, and biocompatibility. For example, surgical instrument handles need to be designed with anti-slip textures and ergonomic curves, while ensuring that the materials are non-toxic and resistant to disinfectants. Pharmaceutical packaging components, on the other hand, need to meet sealing requirements to prevent drug deterioration.
Mold development is the physical realization of the design. Mold design must consider material fluidity, shrinkage rate, and draft angle to prevent product defects such as shrinkage, flash, or deformation. Taking liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding as an example, the mold needs to use a high-precision hot oil mold temperature controller to control the temperature, ensuring uniform vulcanization reactions. The parting surface needs to be designed with precision venting slots to prevent air entrapment, which can lead to product defects. Mold processing relies on high-precision CNC machine tools and electrical discharge machining (EDM) technology to ensure that the dimensional accuracy of the core and cavity reaches within ±0.01mm.
2. Raw Material Selection and Pre-treatment: The Source of Quality
Medical injection molding places extremely stringent requirements on raw materials. Commonly used materials include polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), polyether ether ketone (PEEK), and liquid silicone rubber (LSR), which need to possess high strength, high-temperature resistance, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties. For example, PEEK is often used to manufacture implantable medical devices due to its excellent radiation resistance and mechanical properties. LSR is widely used in components such as catheters and sealing rings due to its softness and sealing properties.
Raw material pre-treatment is a crucial step to ensure product quality. Plastic pellets need to be dried to remove moisture and prevent air bubbles during injection molding. For materials that are prone to hydrolysis at high temperatures (such as PC), the drying temperature needs to be controlled between 120-130°C, with a moisture content below 0.02%. In addition, raw materials also need to undergo color matching and dust removal treatment to ensure consistent product appearance and the absence of impurities.
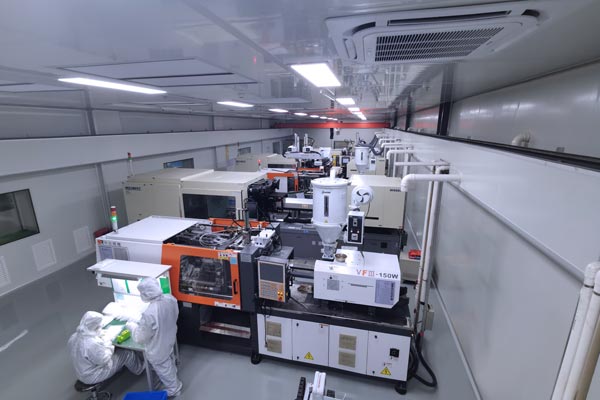
3. Injection Molding: The Core of Precision Manufacturing
Injection molding is the core step of medical injection molding, which can be divided into five stages: mold closing, filling, packing, cooling, and ejection. Taking a vertical injection molding machine as an example, its top-and-bottom mold opening and closing method is more conducive to placing inserts (such as metal nuts and plastic tubes) for integrated molding.
-
Mold Closing and Filling: After the mold is closed, the molten plastic is injected into the cavity under high pressure. The filling speed needs to be adjusted according to the product structure: thin-walled parts require high-speed filling to reduce the thickness of the cooling and solidification layer and avoid weld lines; thick-walled parts, on the other hand, require low-speed filling to prevent shrinkage. For example, the injection molding of medical tubes requires multi-stage injection control, with high-speed filling of the main body in the initial stage and low-speed encapsulation of the inserts at the end to ensure sealing.
-
Packing and Cooling: After filling is completed, the packing stage continues to apply pressure to compensate for plastic shrinkage and increase density. The packing time needs to be set according to the material properties and product thickness until the gate solidifies and seals. The cooling stage is achieved through cooling water circuits inside the mold, and the design must ensure temperature uniformity (within ±5°C) to prevent product warping and deformation. For example, the cooling time of LSR injection molding needs to be precisely controlled to prevent under-vulcanization, which can lead to performance degradation.
-
Ejection and Post-processing: After cooling and solidification, the product is ejected using ejector pins or stripper plates. Medical products have extremely high requirements for ejection quality, and it is necessary to avoid ejection marks, deformation, or scratches. After ejection, the product needs to undergo deburring, cleaning, and surface treatment (such as painting and electroplating) to improve its appearance and functionality. For example, surgical instrument handles need to be treated with anti-slip textures to enhance grip stability.

4. Quality Inspection and Packaging: Strict Checks
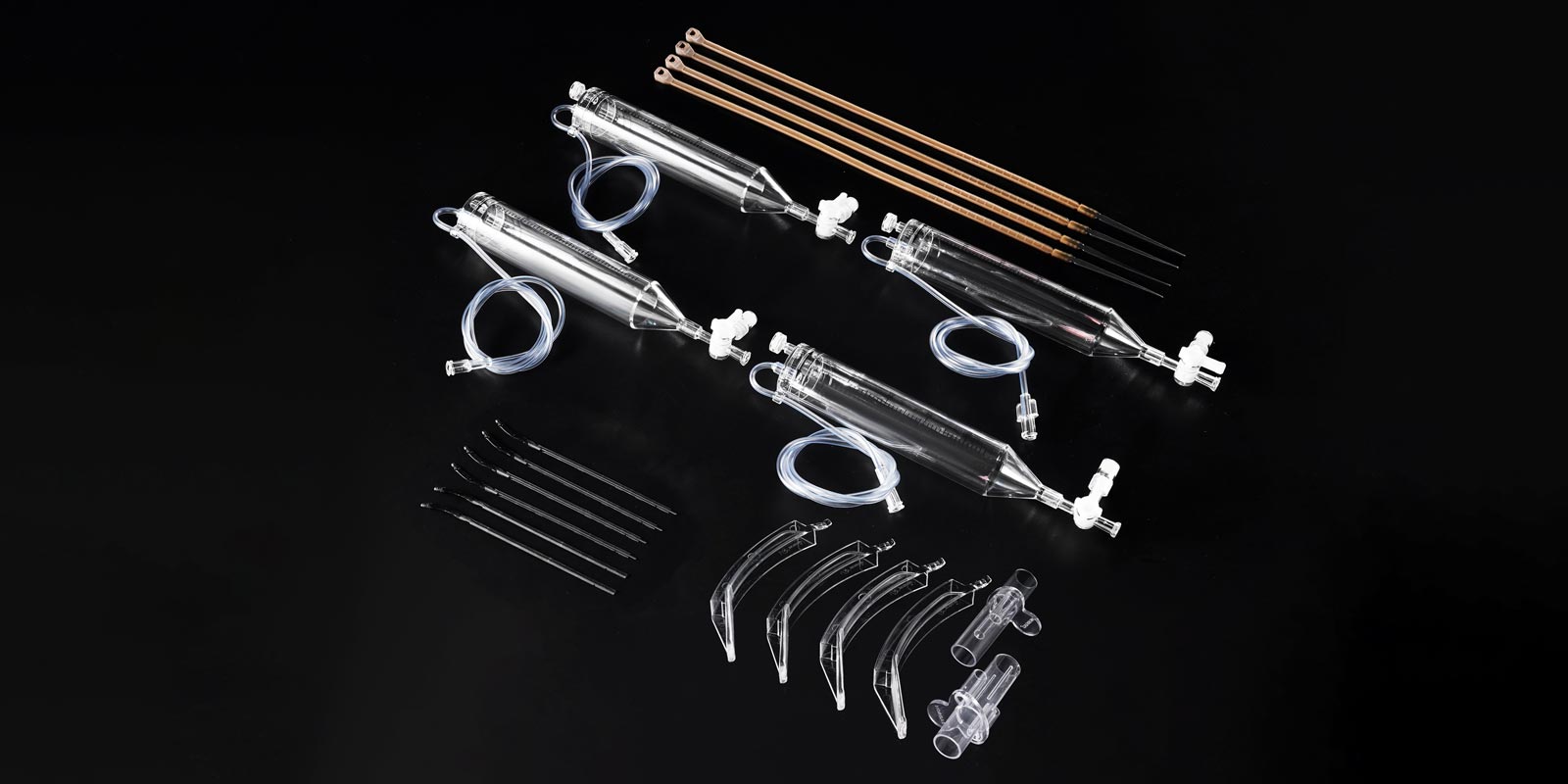
Quality inspection in medical injection molding runs through the entire process, covering four dimensions: dimensions, appearance, performance, and biocompatibility. Dimensional inspection uses coordinate measuring machines to ensure that products meet design tolerances; appearance inspection combines manual visual inspection with automated optical inspection (AOI) to detect defects such as flash, shrinkage, and weld lines; performance inspection includes tensile testing and chemical resistance testing to verify the mechanical strength and durability of products; biocompatibility testing is conducted in accordance with ISO 10993 standards to ensure that materials are non-toxic and non-allergenic.
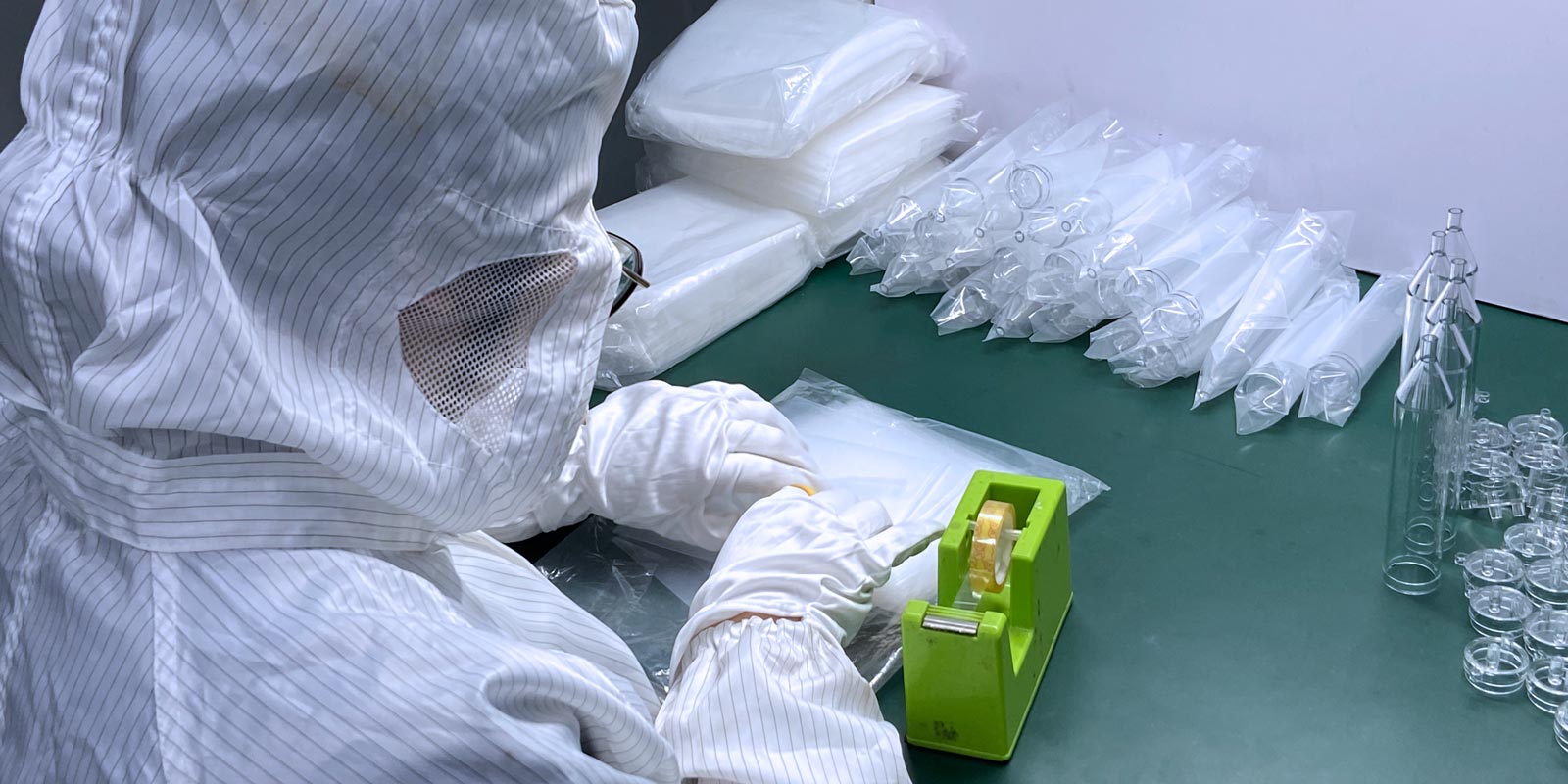
Qualified products need to be packaged in clean rooms to prevent microbial contamination. Packaging materials need to have moisture-proof and anti-static functions to ensure that product performance remains stable during transportation and storage. For example, the packaging of disposable medical devices needs to meet sterility requirements and adopt a double-layer sealing design, with medical dialysis paper for the inner layer and a composite film for the outer layer.
5. Case Study: Injection Molding of Surgical Instrument Handles
Taking the injection molding of a certain brand of surgical instrument handles as an example, its process is as follows:
-
Design Stage: Use CAD software for 3D modeling and optimize the grip curve and anti-slip textures; the mold design adopts a hot runner system to reduce material waste.
-
Raw Material Selection: Select medical-grade PP material, which possesses high strength and resistance to disinfectants; the drying temperature is controlled between 80-85°C, with a moisture content below 0.1%.
-
Injection Molding: Use a vertical injection molding machine, with two-stage injection during the filling stage. High-speed filling of the main body in the initial stage and low-speed encapsulation of metal inserts at the end; the packing pressure is set at 120 MPa, and the cooling time is 15 seconds.
-
Quality Inspection: The dimensional tolerance is controlled within ±0.05mm; appearance inspection uses an AOI system to detect weld lines and flash; performance testing includes 1000 cycles of grip fatigue testing and 72 hours of disinfectant immersion testing.
-
Packaging and Shipment: Packaging is carried out in a Class 10,000 clean room, using anti-static bags and foam boxes for double protection to ensure sterile transportation of products.
Conclusion
Medical injection molding is a systematic project that integrates material science, precision manufacturing, and quality control. From product design to mold development, from raw material selection to injection molding, every step must strictly adhere to industry standards and process specifications. With the continuous advancement of medical technology, injection molding technology is developing towards higher precision, higher efficiency, and greater environmental friendliness, providing stronger support for medical equipment manufacturing.













 Home
Home
