In the field of medical device injection molding, laryngoscope injection molding stands out due to its anatomical adaptability, functional integration requirements, and the particularity of clinical application scenarios. Every link, from material selection to mold design, from functional realization to sterilization requirements, needs to meet the high standards of clinical scenarios in otolaryngology and anesthesiology.
I. Material Selection: Dual Constraints of Biocompatibility and Functionality
The core components of laryngoscope injection molding - the viewing lens and the housing - require medical-grade polymer materials, with polycarbonate (PC) and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS) being the mainstream choices. PC is the preferred material for the main body of the viewing lens due to its high transparency, strong impact resistance, and high-temperature resistance, ensuring light transmittance and structural stability. ABS, on the other hand, is often used for housing manufacturing because of its high strength, ease of processing, and low cost. Some high-end products use polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) or optical fiber bundles to transmit light, ensuring an illuminance of ≥1300 Lux to meet clinical observation needs.
Compared with other medical device injection molding, laryngoscope materials need to meet two additional key standards: First, biocompatibility, which must comply with the YY/T 0819-2010 "Disposable Laryngoscope Blades" standard to ensure non-toxicity and non-allergenicity. Second, sterilization compatibility, where the materials must withstand ethylene oxide sterilization, and the residual ethylene oxide after sterilization should be ≤10 μg/g. For example, disposable laryngoscope blades need to undergo a strict sterilization process, while the requirements for sterilization residue in ordinary injection-molded products (such as medical plastic trays) may be more lenient.
II. Mold Design: Challenges of Complex Structures and Precision Manufacturing
The complexity of laryngoscope injection molds is reflected in three dimensions:
-
Anatomical Adaptability: Laryngoscopes need to be designed according to the anatomy of the human pharynx and larynx, with the thickness and curvature of the blades matching different models from 0# newborns to 4# adults. For example, the thickness of a neonatal laryngoscope blade needs to be controlled within 1.2 mm, and its curvature should fit the narrow glottic structure of newborns, while adult models need to balance strength and comfort.
-
Functional Integration: Modern laryngoscopes integrate functions such as CMOS sensors, LED light sources, image freezing, and measurement annotations. The mold needs to reserve installation positions for sensors, optical fiber channels, and circuit interfaces. For example, the Glidescope video laryngoscope has a fully enclosed blade structure with built-in cameras and optical cables, requiring the mold to ensure airtightness to prevent external contamination.
-
Cooling System Optimization: The top space of the laryngoscope blade is narrow, making it difficult for traditional mold cooling water channels to cover deep holes, resulting in uneven mold temperature and product deformation. The 3D-printed conformal cooling water channel technology designs a water channel system covering the mold cavity by simulating fluid dynamics, reducing the molding cycle from 20 seconds to 12 seconds and decreasing product deformation by 0.5 mm. For example, the laryngoscope molds manufactured by Hanbang Technology using 18Ni300 mold steel powder through metal 3D printing have significantly better mold temperature uniformity than traditional beryllium copper molds.
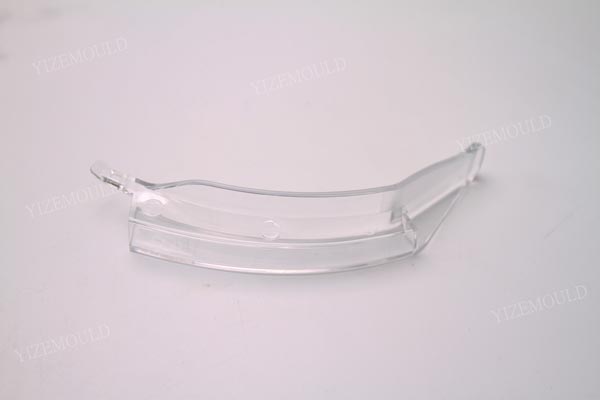

III. Functional Realization: Technological Breakthroughs in Visualization and Intelligence
The functional evolution of laryngoscope injection molding reflects the transformation of medical devices from "structural tools" to "intelligent systems":
-
Visualization Technology: Traditional rigid laryngoscopes rely on direct observation, while visual laryngoscopes transmit the structure of the pharynx and larynx to a display screen through a high-definition camera (with a resolution of up to 1080P) and an LED light source at the end of the blade, enabling visualization of the intubation process. For example, the visual laryngoscope from Mole Medical integrates a high-power LED light source and a high-definition camera at the end of the blade, providing a blind-spot-free view from the entry of the laryngoscope into the mouth to the glottis, increasing the intubation success rate by 22%.
-
Intelligent Assistance: AI-assisted diagnostic systems can mark suspicious lesion areas in real time, reducing the missed diagnosis rate. The image freezing function allows doctors to complete operations at the best viewing angle, and the measurement annotation function can quantify lesion sizes, providing data support for treatment. For example, trial data from a hospital shows that the AI-assisted system increased the early detection rate of laryngeal cancer by 18%.
-
Modular Design: To reduce long-term use costs, laryngoscope injection-molded products adopt a modular design, such as replaceable light sources, lenses, and battery components. For example, some fiber laryngoscopes support the optional installation of NBI (narrow-band imaging) functional modules to improve the early detection rate of laryngeal cancer.
IV. Sterilization and Cost: Balancing Disposable Use and Economy
The sterilization requirements for laryngoscope injection molding are much higher than those for ordinary medical devices:
-
Disposable Use Trend: To reduce the risk of cross-infection, disposable laryngoscope kits have become the first choice during peak outpatient and emergency hours. Their injection molding process needs to balance cost and performance. For example, the cost of a viewing lens made of PC/ABS composite material can be controlled at 3-5 yuan per piece, while the sterilization cost of a reusable laryngoscope may be as high as 20 yuan per time.
-
Long-term Maintenance Cost: Reusable laryngoscopes require regular cleaning of the optical fiber channels and replacement of anti-fog coatings, and the hinge structure of the laryngoscope body needs to be tested for a service life of over 50,000 times (such as using aviation-grade aluminum alloy materials). In contrast, low-end ABS plastic bodies are prone to joint loosening, significantly increasing maintenance costs.
V. Industry Trends: Integration of Minimally Invasive and Intelligent Technologies
The future development directions of laryngoscope injection molding focus on two major technological trends:
-
Minimally Invasive: By reducing the diameter of the laryngoscope body (such as 2.4-3.6 mm fiber laryngoscopes) and optimizing the bending angle (such as a 60°-90° field of view design), the damage to the pharyngeal and laryngeal mucosa of patients is minimized.
-
Intelligence: Wireless medical laryngoscopes connect to hospital information systems via Bluetooth/WiFi, enabling one-click generation of examination reports. 5G technology supports remote consultations, allowing patients in remote areas to access high-quality medical services. For example, a certain wireless laryngoscope product has achieved an image delay rate of <0.1 second, meeting the requirements for real-time diagnosis.
As a high-precision branch in the field of medical devices, laryngoscope injection molding has strict requirements in terms of material selection, mold design, functional realization, and sterilization. From traditional rigid laryngoscopes to intelligent video laryngoscopes, and from single structural tools to multi-functional diagnostic systems, the evolution path of laryngoscope injection molding not only reflects the development trend of the medical device industry but also provides key support for improving medical efficiency and patient experience.













 Home
Home
