In the field of medical plastic injection molding, when the molded parts have side convex-concave structures (including external threads), if a side core-pulling structure is not adopted and only push rods or push plates are used for demolding, the plastic molded parts will undergo elastic deformation, forcing the plastic parts out of the injection mold. This demolding method is defined as forced demolding.
Compared with side core-pulling demolding, forced demolding has a relatively simple structure. It is mainly suitable for plastic injection-molded parts with small side undercut dimensions, side undercut structures with large-angle slopes, and relatively low precision requirements. In medical injection molding production, for some components with relatively loose requirements for dimensional accuracy and surface quality, forced demolding can take advantage of its simple structure to reduce mold manufacturing costs and shorten production cycles. However, forced demolding is not without risks. Improper operation may lead to deformation or damage of the molded parts, affecting product quality and production efficiency.
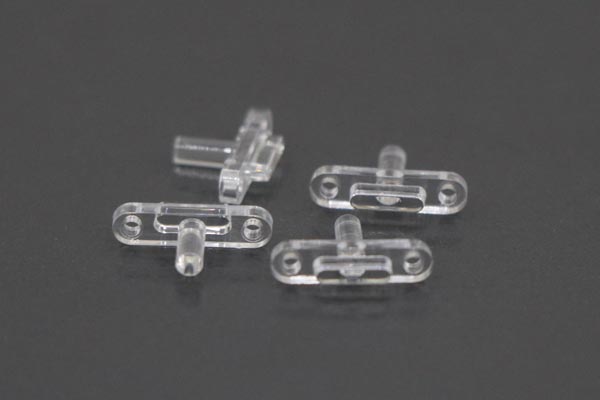

Common Types and Application Scenarios of Forced Demolding Secondary Demolding Structures
-
Spring Secondary Demolding Structure
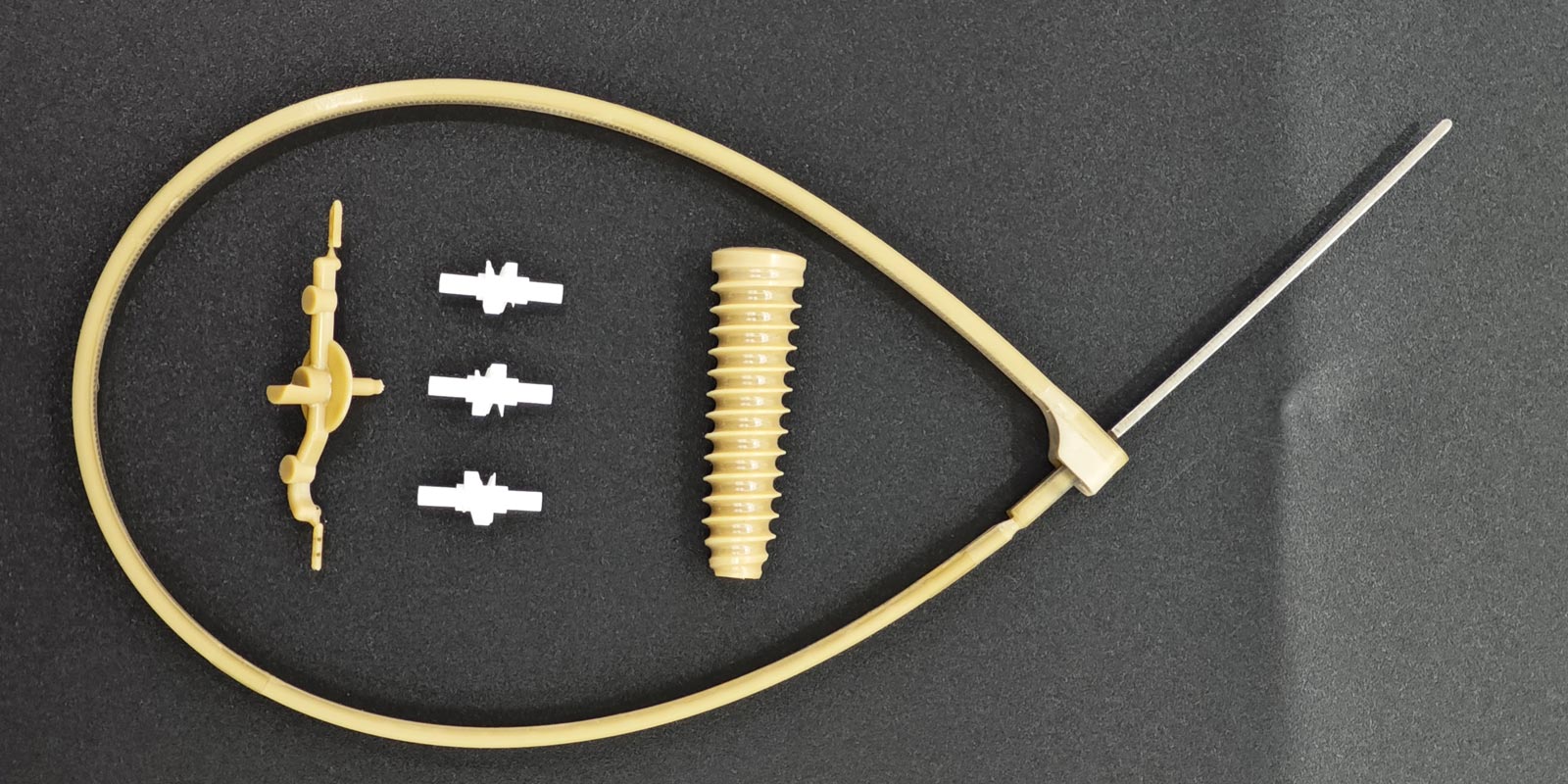
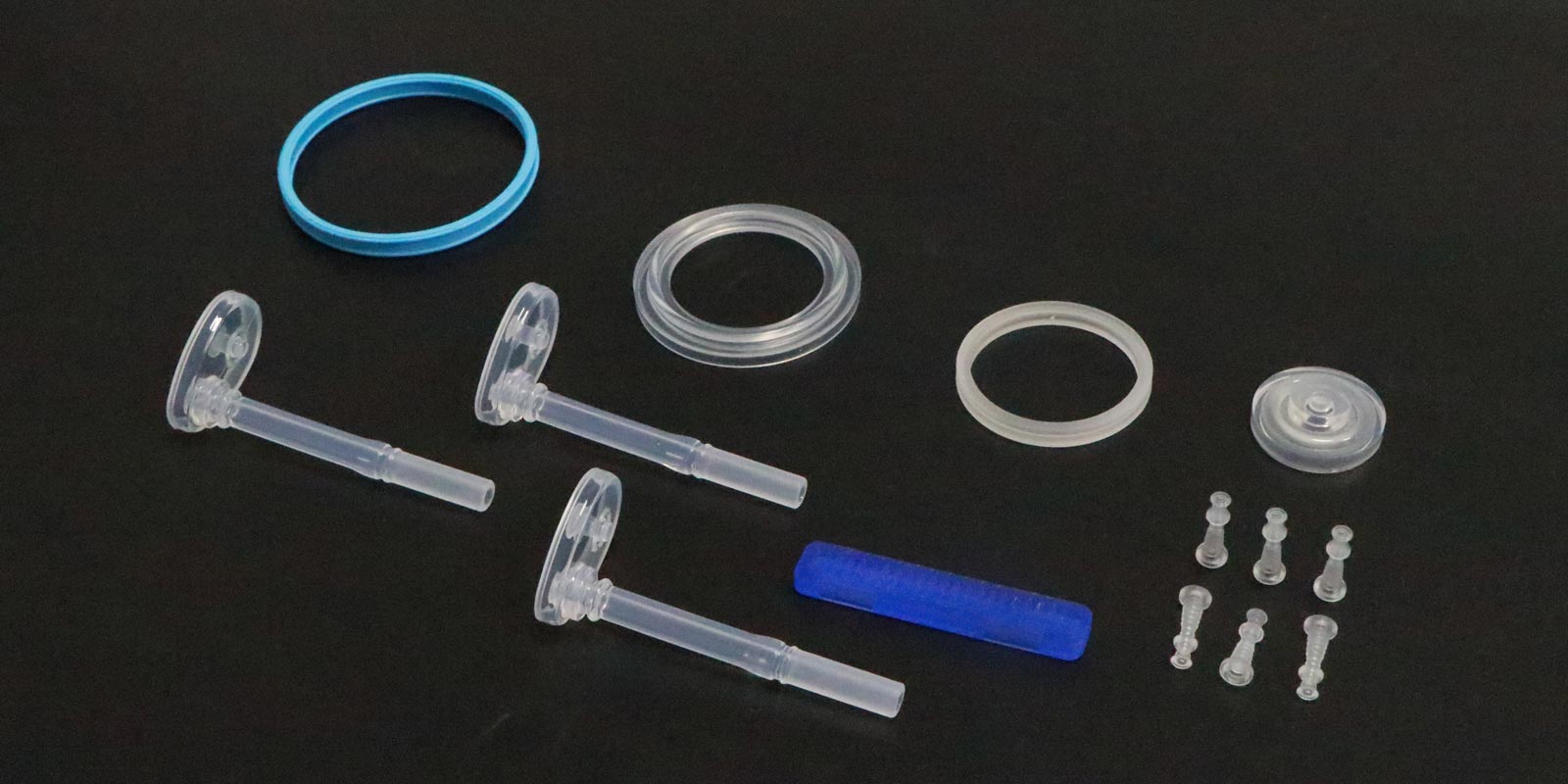
This structure is suitable for plastic injection-molded parts with a relatively simple structure but with one undercut, where internal core-pulling cannot be adopted and forced demolding is required. It utilizes the elastic force of the spring to provide an additional pushing force for the molded parts during the demolding process, helping them to smoothly separate from the mold. The selection and installation position of the spring are crucial. They need to be precisely calculated and designed according to factors such as the size, weight of the molded parts, and the strength of the undercut. If the spring force is insufficient, incomplete demolding may occur; if the force is too large, it may cause deformation or damage to the molded parts. In medical injection molding, for some small and lightweight medical accessories with undercuts, such as certain plastic connectors and joints, the spring secondary demolding structure can function well.
-
Movable Core Secondary Demolding Structure
When there is an undercut in the center of the plastic product and forced demolding must be adopted, the movable core needs to be extracted before forced demolding. The design and motion control of the movable core are the keys to this structure. The movable core is usually driven by inclined guide posts, oil cylinders, and other driving devices to achieve extraction and reset actions. During the mold design stage, the motion stroke and extraction time of the movable core need to be precisely calculated to ensure that it can be smoothly extracted during the demolding process without interfering with the molded parts. At the same time, the material selection of the movable core is also very important. It needs to have good wear resistance and corrosion resistance to ensure stable performance during long-term use. In medical injection molding, for some medical products with complex internal structures and central undercuts, such as certain plastic containers and medical device housings, the movable core secondary demolding structure can effectively solve the demolding problem.
-
Typical Structure of Double (Group) Push Piece Fixed Plate Secondary Demolding Mechanism
The double (group) push piece fixed plate secondary demolding mechanism is a relatively complex demolding structure. It achieves secondary demolding through the coordinated movement of two groups of push piece fixed plates. This structure can provide a more stable and uniform demolding force, suitable for medical injection-molded parts with high demolding force requirements and complex structures. During mold design, the movement sequence and stroke of the two groups of push piece fixed plates need to be reasonably designed to ensure that the molded parts can smoothly separate from the mold during the demolding process without getting stuck or damaged. At the same time, this structure also has relatively high requirements for mold processing accuracy and assembly. It is necessary to strictly control the quality of each link to ensure the normal operation and service life of the mold. For some large and high-precision medical injection-molded parts, such as certain plastic surgical instruments and medical equipment housings, the double (group) push piece fixed plate secondary demolding mechanism can provide a reliable demolding solution.
In medical injection molding production, to solve the demolding problem caused by undercuts, it is necessary to reasonably select a forced demolding secondary demolding structure according to the specific structure and production requirements of the molded parts. At the same time, during mold design, manufacturing, and use, it is necessary to strictly control the quality of each link to ensure the smooth progress of the demolding process, thereby improving the quality and production efficiency of medical injection-molded parts.













 Home
Home
